Tuesday, September 29, 2015
Legacy of Learning: Cells
I have uploaded your Cell LoL documents. Click here to view the documents.
BioChem folder Available on Google Drive
If you want to check out your LoL Projects I have added the scanned documents to a Google Drive Folder. While you are at it feel free to add the pdfs to the appropriate Live Binder pages (you know, in all your free time). Click here for the link to the folder!! You should be able to click on each document for a better view.
Monday, September 28, 2015
Metabolism & Enzyme Notes
My version of the notes is available on Google Drive. The notes are not divided by section of the book, you will have to go through to book also.
Wednesday, September 23, 2015
7.3 Passive Transport
Passive transport is diffusion of a substance across a membrane with no energy involved. Diffusion is the movement of molecules of any substance so that they spread out evenly into the available space. 
The movement of particles will flow from high concentration to low concentration. Note, to go from low to high you need energy in the from of ATP to move the solute against its concentration gradient.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane. This is especially important when the solute particles are too big to flow through the membrane. In this case the water moves to equalize the concentrations.
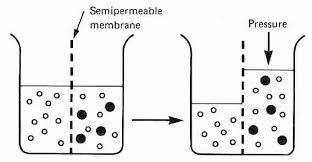
Tonicity is the ability of the surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water.

There are many examples of diffusion, some of which include proteins, and this process is vital to cell function and overall health.
Tim Barber
The movement of particles will flow from high concentration to low concentration. Note, to go from low to high you need energy in the from of ATP to move the solute against its concentration gradient.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane. This is especially important when the solute particles are too big to flow through the membrane. In this case the water moves to equalize the concentrations.
Tonicity is the ability of the surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water.
There are many examples of diffusion, some of which include proteins, and this process is vital to cell function and overall health.
Tim Barber
6.5 study guide
6.5- Study Guide
1.) The theory that an early ancestor of eukaryotic cells engulfed an oxygen-using nonphotosynthetic prokaryotic cell is? Endosymbiont Theory
2.) Mitochondria is the site of what? Cellular Respiration
3.) Infoldings in the inner membrane that prevent it from being smooth are called? Cristae
4.) Site of photosynthesis that contains green chlorophylls is called? Chloroplasts
5.) Flattened, interconnected sacs that make up another membranous system inside of chloroplast are called? Thylakoids
6.) What do peroxisomes do? Take toxins and convert them to water
Tuesday, September 22, 2015
Friday, September 4, 2015
5.4 Proteins
Proteins are large macro molecules consisting of one or more long chains of Amino Acids(Polypeptides). Proteins have several functions in the body. They speed up chemical reactions(enzymes), defend the body against foreign agents(antibodies), communicate between cells or coordinate processes(messengers), provide structural support, and they can store and transport 'Nutrients'.
TRB
TRB
Thursday, September 3, 2015
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)